Last week was great! Piggy energy, a lot of ideas and projects, and all are fulfilled! Which one to take?! Everyone without exception people are sociable, kind and responsive. Life is Beautiful! The inspirational soul soars, sings and rejoices! And suddenly, the decline is heavy, muddy, protracted. Hopelessness, depression. So the hypomania is expressed: From total positive - to total negative. The disease has its own symptoms and treatment.

What it is?
Goloman In Psychology - The state of similar mania, but flowing into less light shapes. It is manifested in a relatively stable, raised mood, occasionally, in a situation accompanied by irritation and anger. The state continues for several days, manifesting the severity of exhaustive satisfaction, absolute productivity, high degree of charge and activity.
Differences from Mania are concluded Absence of psychotic symptoms and raising, sometimes quite productive, efficiency and adaptation. Often it can occur in the form of a bipolar disorder phase.
In other cases, hypologia functions against the background of failures in the activities of the nervous system, with hyperthyroidism, intoxicating psychotrops or as side effects when receiving some medicines (antidepressants).
In accordance with the formal definition on the ICD-10, the state is characterized by an overly positive or irritable attitude, clearly atypical for a particular individual, which is at least within four days.
Thus, Hypologania as an affective disorder is a hidden form of mania occurring in the absence of pronounced arousal. At the same time, explicit behavioral disorganization or retreats from the norms of social behavior of the individual does not occur, since the symptoms of psychosis (delusibility, hallucinations, etc.) is not present.
Mood disorders were also observed by hippocrates (V century BC), divided them to melancholy and mania. Later, in the works of E. Fucket, these states took to the manic-depressive psychosis (TIR).


Conceptually this definition has been preserved for almost the entire XX century.
In about the 60s of the XX century. A number of scientists have noted some heterogeneity of the state group, within which the monopolar and bipolar forms determined. Later psychologists have allocated two types of TIR:
- For 1 type Characteristically alternating episodes of depression and mania (sharply increased mood, leading to serious violations of the functionality of the body);
- For 2 types Characterized alternations of depressive states exclusively with hypologies (without serious violations).
Since 1990, ICB-10 has been distinguished by 3 severity of mania - hypologia, mania in the absence of psychotic symptoms, mania with psychotic symptoms.
It is noteworthy that Ludwig Van Beethoven, Virginia Wolfe, Ernest Hemingway, Isaac Newton, Judy Garland, Robert Schuman and a number of other ingenious people and a number of other ingenious people.
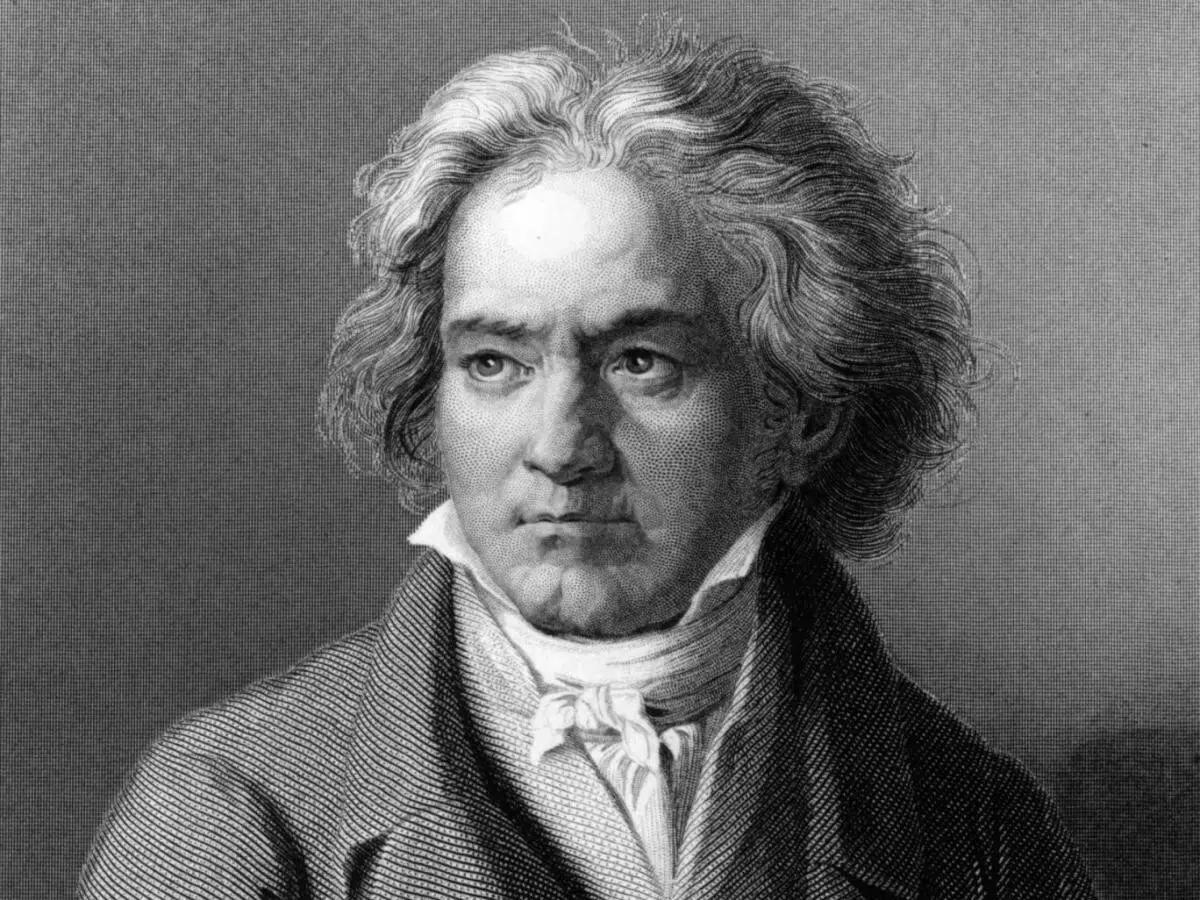
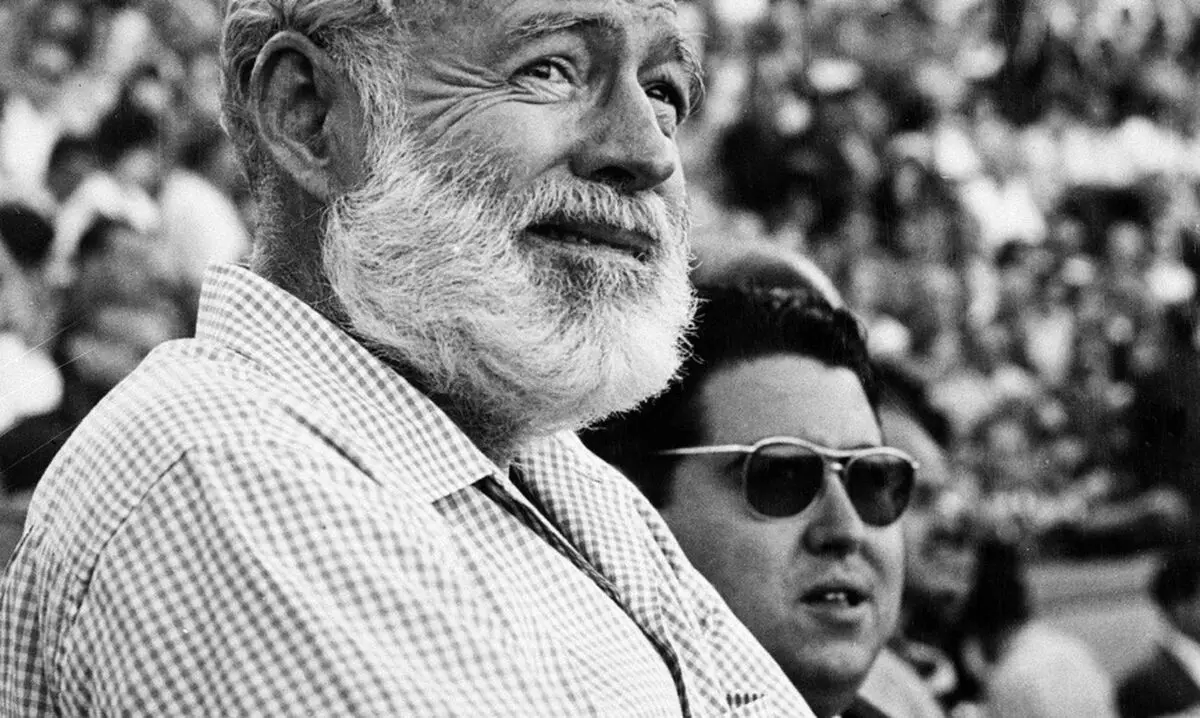


At one time, doctors diagnosed TIR N. S. Khrushcheva, whose nearest environment watched how often his fun and joyfulness was replaced by a deep melancholy.
Traditionally, the violated mood is considered to be episodic if its duration is about a week.
In case of hypomanical states, most of those experiencing disorder do not belong to the patient, therefore does not appeal to doctors. It is for this reason that there is no reliable statistics of disorder. The unrecognition of affective disorder leads to a deterioration of the situation.
Out of reasons It is characterized by violations and affective, and somatopsychiatric spheres. A stable raised mood match the overestimated total tone, a sense of well-being and excessive optimism. Own merits and originality exaggerate, prevail the ideas of excellence, there is no critical attitude towards himself.

Disagreement or objections from the environment provoke anger. In general, the state, like his signs, is characterized by lability.
The process of thinking in such a person is diminishing, the speech loses its delicacy and expressiveness. Inexhaustible energy and some disgracefulness stimulate the appearance of emotional lifting in the performance of even ordinary and routine work. The person inspires the implementation of many plans, without thinking about the reality of their implementation.
For a patient, a high threshold of fatigue and sustainability to significant loads is characterized. Reduced need for rest and sleep. In this case, somatic signs can dominate. Possible protracted disorder.
In its cyclotimic periods, hypologia proceeds to a sufficiently distinctly, with pronounced lifts and deposits of mood. In cases of a protracted option noted Resistance to affect.

Atiypical patterns of the process are likely - the emergence of ultra-subject formations, obsessions, depressive-pain syndromes.
With relatively even manifestations of the disorder, temporary somatopsychological manifestations may occur in the form of vegetative crises, vital fears, asthenia, etc. More often, hypologia occurs within a bipolar affective disorder (bar), where it is usually replaced by depression, forming or continuous continuum, or cyclicity. The bipolar form of disorder is often distinguished by early manifestations (in children or and adolescence) and a chronic form of a flow, which may be:
- Remisted (episode - remission - episode);
- with dual phases (one episode is immediately replaced by the opposite direction);
- Continual (periods of remission between episodes are absent).
Normal remission occurs in a small number of patients. The disease can go to a more pronounced state - mania. The average duration of episodes is in the range of 2 weeks to 2 months.
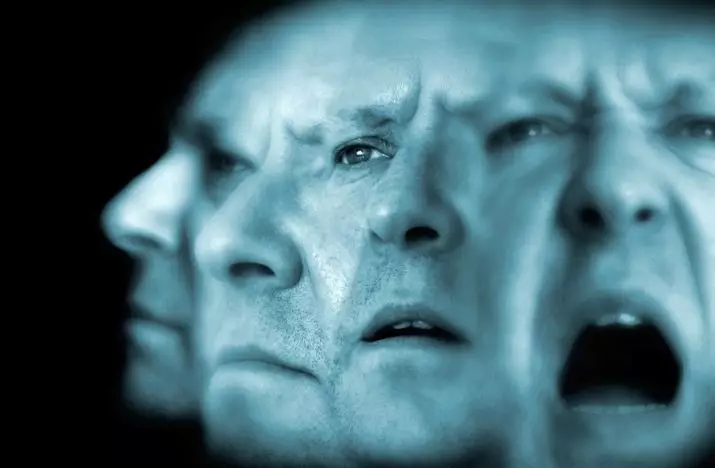

For the rhythmic pattern of the appearance of episodes, spontaneity is characterized, which leads to a patient a sense of insecurity.
Bar believed to disability diseases. In addition, with bipolar disorders, the risks of suicide increase significantly.
Varieties
Several varieties of hypologia distinguish:
- simple ("funny");
- irritable or angry, expansive.
Depending on the personal disorders accompanying hypologia:
- CVRUULENT (with an insurmountable desire of the patient for southeticity, constantly struggling for "filtered" rights);
- adventuristic (tendency to adventures);
- dysforic (irritability, replaced by a feeling of longing, tension, tendency to aggressive behavior).
According to the influence of hypologia to the somatopsychic sphere, atypical hypologia (euphoric hypochondria) is also isolated, the flow of which is accompanied by increased mood and unrestrained activities aimed at overcoming imaginary illness.
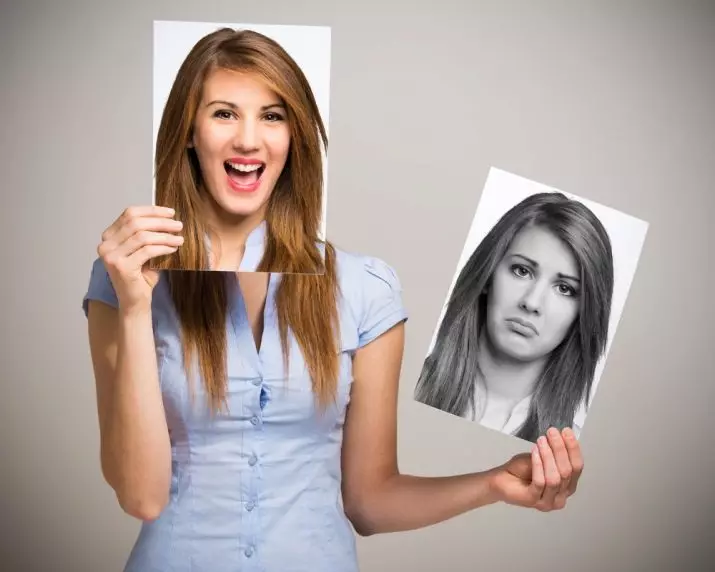

As a characteristic severity of symptoms, allocate:
- pure (explicit) form of hypologia;
- Hidden hypomania (embossing form).
There is also the so-called productive form of hypologia, observed during cyclotimia, characterized by infrequent failures of the "Sleep - Wake-up" cycle and accelerating ideator processes.
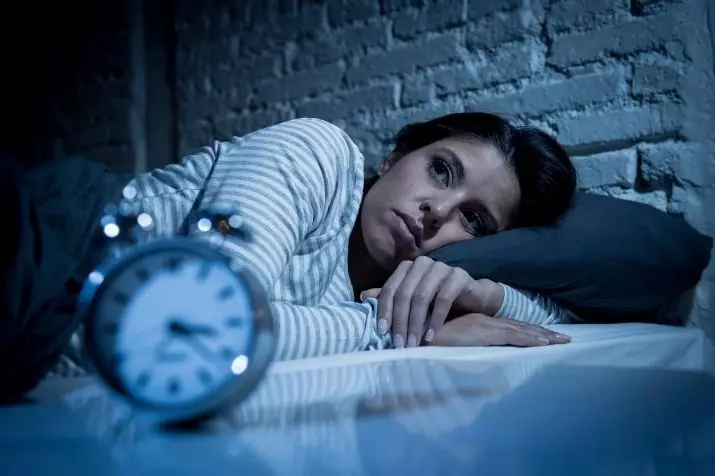

Causes of occurrence
The emergence of hypologia contributes to a number of reasons.
- Overly active work of the thyroid gland, accompanied by increased methods of hormone. Protect the disorder by postpartum syndrome and climax.
- Episodes of hypologia are manifested both as a phase of food excitation. The reasons may be anorexia or therapeutic starvation.
- Leads to a disease and reception of some drugs (opiates, baclophen, a fenamine, captopril, bromcriptein, bromide, cimetidine, cyclosporine, corticosteroids, yohimbin, teturas, hallucinogens).
- In cases of cutting cancellation of antidepressants.
- With excessive reception of stimulants (energypath, cocaine, coffee, etc.).
- Cases of organic brain damage (infectious and noncommunicable nature).
- Bipolar affective disorders (TIR), the emergence of which stimulate hereditary factors and stress.
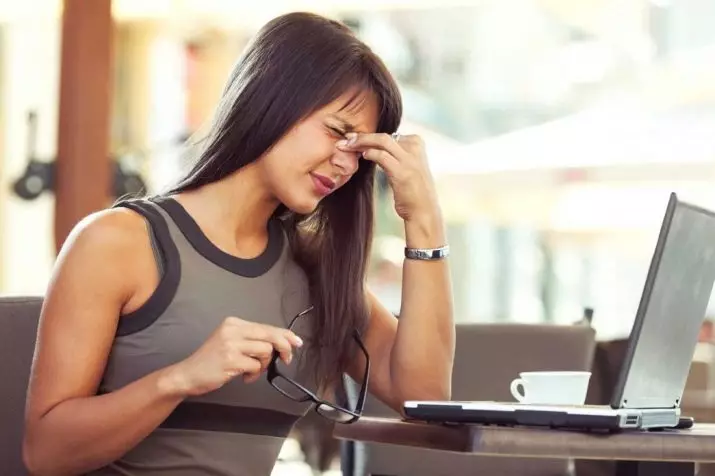

How does it manifest?
Symptoms of hypologia include:
- Ultipical indemid-irritable mood, persistent for several days;
- Unusual spelling and susceptible pace of speech;
- improving the level of physical activity;
- Reducing the level of needs in holiday and sleep;
- scattered attention;
- manifestations of recklessness and inadequate situational behavior;
- anomalously high degree of sociability and episodes of familiarity in communication;
- Growing sexual entry.
Hidden forms of hypologia manifest their appearance by deflecting (in children's and adolescence), Bulimia, nymphomania and satyriasis. The episodes of high creative productivity are likely, accompanied by a sense of inspiration.

In hormonal disorders, an elevated temperature (37-38 °) is added to the previously listed symptoms.
Signs of hypologia caused by hyperthyroidism are tremors and a symptom of Gref ("Symptom of the Settlement Sun"). Often hypomania is accompanied by an increase in appetite.
For children's hypologia characteristic of the manifestation:
- fussiness and explicit expressed motor dismissal;
- impulsivity;
- disobedience and unusual stubbornness;
- grimensions;
- multi-absorption;
- tendency to coarse leaving;
- frightening;
- A sharp increase in instincts and deposits (voraciousness, onanism).

Diagnosis and treatment
The main criteria for the diagnosis of disorder are considered an excessive or irritable mood for at least 4 days.
For reliable diagnosis, tests use tests, and at least 3 symptoms of the list below should be detected as necessary and sufficient:
- high level of activity or anxiety;
- excessive talkative;
- difficulties with focusing or high distractions;
- reduced need for rest and sleep;
- elevated libido;
- Small couments or reckless actions, irresponsible behavior;
- Excessive sociability with manifestations of familiarity.
Due to the fact that hypologia is provoked by different reasons, a differential diagnosis is carried out in psychiatry. If the episode of the hypomania is provoked by the adoption of psychoactive means, the signs of intoxication accompanimate.

The patient has a changed size of pupils, tremors and vegetative reactions.
Children disorder manifests itself mainly on the psychomotor level of response, due to the fact that at this age, maniacal states are more atypical forms than in adults. It is important to take into account that for preschool and younger schoolchildren, cheerfulness, activity and lability, the mood manifested under the influence of many internal and external order factors are regulatory. It is for this reason that hypologia in children are suggested with long-term euphorids, accompanied by impulsive and rude violations of behavior.
With such causes of disorder, as hyperthyroidism or poisoning with psychoactive agents, therapy is to eliminate these reasons (thyreostatic preparations, surgical treatment, etc.) are used.
In cases of bipolar disorders, normatimics are used (mood stabilizers):
- For example, lithosan or lithobide (dosage strictly individual, the smallest dose is 0.6 mmol / l);
- Anticonvulsant drugs (Valproate, Carbamazepine, Gabapentin, Okskarbazepine, Topiramat, etc.).
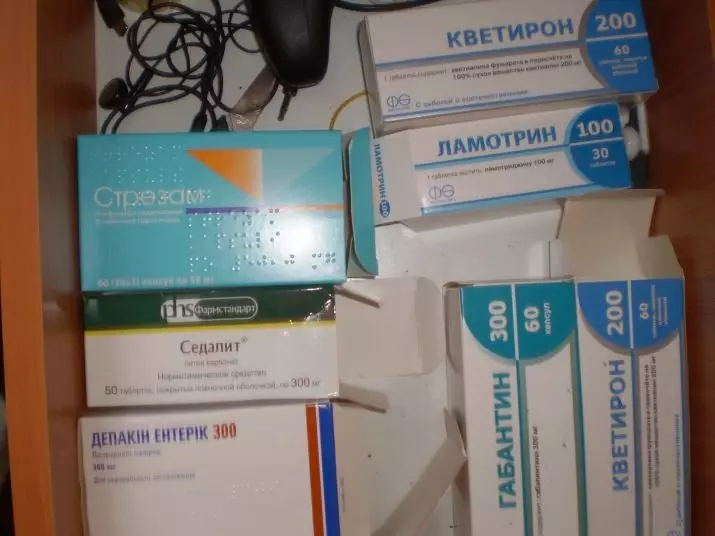
The second group of drugs can be used in combination with the first.
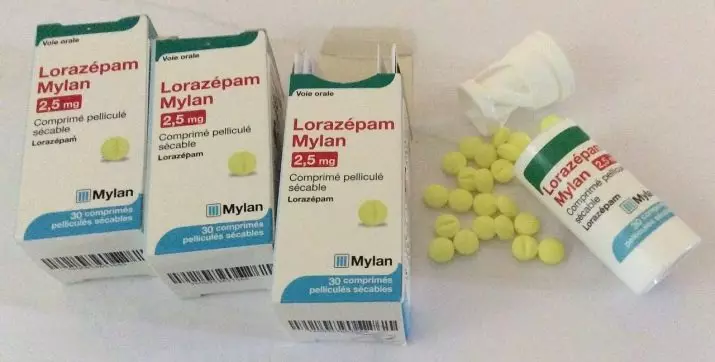
With insomnia prescribe Benzodiazipins (clonazepams, lorazepam). As they lead to addiction, they use a short period of time. Sometimes the sedatives are prescribed (Skipidem). Children are more often prescribed Lithium preparations.
Valproate application needs In the close observation of the doctor. This medicine can lead to hormonal changes in teenage girls and ovarian polycystic syndrome in young women.
For more effective treatment of bipolar disorder, it must be accompanied by frequent replacement of drugs with the direct participation of the doctor . Preparations of stabilizing purposes can be applied for years.
The episode of the hypomania is born with lithium preparations in small and medium doses.
Support for norms is usually carried out in the initial period of relief period, since the prophylactic effect of these drugs is slow. Antidepressants may increase the severity of bipolar disorder. In these cases, the use of the drug refuses. In cases where normatimics are not sufficiently effective in therapy include atypical antipsychotics.

What is dangerous hypomania?
Bipolar disorder with a phase of hypologia provides compulsory treatment, since stable hyperactivity naturally leads to the depletion of the body, apathy and deep depressive states. Goloman is fraught with dangerous consequences.
- Sleep deficit leads to a significant overwork of the body. The level of attention and memory falls.
- Possible overeating leads to the obesity and development of avitinosis. The body's protective forces fall, chronic diseases are sharpened.
- The coming periods of apathy complicates self-control and creates additional vital problems.
- A series of days of excessive activation is replaced by deep depressive and rather long-term, up to several months, periods. The neglence of hypologia leads to decay forces. Adequate reality perception is violated. A person becomes conflict that leads it to social isolation.

Often, hypologia takes place in creative people. In general, some cases of well-known writers, poets, composers, artists for a long time (months) fell during periods of inspiration, creating masterpieces of art. However, the raising periods were certainly replaced by depressions and a significant decline.
Attempts to return radiant inspiration, using alcohol or narcotic drugs, lead to an absolute deterioration in the situation.
About ten signs of Mani look next.
